Table of Contents
Ozempic Dosing Frequency Guide
Ozempic has surged in popularity as a game-changer for managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss, especially in the US where chronic conditions affect millions. This ozempic dosing frequency guide provides essential insights into its administration, helping patients navigate treatment with confidence and clarity.
Ozempic, known generically as semaglutide, is an FDA-approved injectable medication primarily used to improve blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes. It also aids in weight management by mimicking a hormone that regulates appetite and insulin. Administered as a subcutaneous injection–meaning just under the skin–Ozempic follows a once-weekly schedule, making it convenient compared to daily pills.
The starting dose for Ozempic is 0.25 mg once a week for the first month, as recommended by FDA guidelines from sources like WebMD. This initial weekly semaglutide administration schedule allows the body to adjust gradually, minimizing side effects while building efficacy. Patients can choose any day for the injection, such as Monday or Friday, but consistency in timing is key for steady results. For detailed progression, refer to the Ozempic Dosing Schedule by Week.
As doses may escalate to 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or higher based on response, understanding semaglutide injection timing tips ensures optimal outcomes. Later sections explore benefits, ozempic side effects weight loss, and ozempic vs wegovy dosage comparisons. Always consult your healthcare provider in the US for personalized advice tailored to your health needs.
Understanding Ozempic Dosing Basics
Ozempic, a semaglutide-based medication, plays a key role in managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss through its GLP-1 agonist properties. Proper adherence to the Ozempic Dosing Schedule is essential for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks. This section outlines the basics to help users follow protocols safely under medical supervision.
Starting Dose and Initial Schedule
The starting dose of Ozempic is 0.25 mg administered once weekly for the first four weeks. This low initial amount introduces the body to the medication gradually, allowing it to build tolerance and reduce the risk of common gastrointestinal issues. As part of the ozempic dosing frequency guide, this phase establishes the semaglutide weekly injection protocol, setting the foundation for long-term use in weight management.
During these initial weeks, patients typically experience milder side effects as the body adjusts. For instance, many report subtle changes in appetite and energy levels without severe discomfort, helping them ease into the GLP-1 agonist dosing timeline. This approach aligns with guidelines from sources like WebMD, which emphasize starting low to optimize tolerance.
Practical tips include marking your calendar for injection days and consulting your physician before beginning. Always store pens in the refrigerator and discuss any early ozempic side effects weight loss concerns promptly to ensure smooth progression.
Weekly Administration Frequency
Ozempic follows a once-weekly administration frequency via subcutaneous injection, ideally on the same day each week to maintain consistent blood levels. As noted in WebMD details, “Administer once weekly on the same day each week,” this schedule supports steady efficacy for blood sugar control and weight loss support.
The injection can be given at any time of day, with or without food, but consistency aids adherence. Rotate sites like the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm to prevent irritation, and if changing days, wait at least 48 hours from the previous dose. For missed doses, take it as soon as possible within five days; otherwise, skip and resume the regular schedule to avoid overlap.
- Use a new needle for each injection to ensure sterility.
- Check the solution for clarity before use.
- Keep the pen at room temperature for 30 minutes prior to injecting.
These steps help maintain the medication’s potency while fitting into daily routines.
Dose Escalation Process
Dose escalation begins at week five, increasing from 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg weekly, with potential further steps to 1 mg or up to 2 mg based on individual response and tolerance. This titration allows the body to adapt, reducing the intensity of side effects while enhancing therapeutic outcomes in diabetes and weight management.
Escalation typically occurs every four weeks, guided by physician assessment of efficacy and side effects. For example, if 0.5 mg effectively controls blood sugar but weight loss plateaus, a move to 1 mg may be recommended. Considerations like ozempic vs wegovy dosage highlight that while both use semaglutide, Ozempic’s steps focus more on glycemic control, often aligning with lower maintenance levels than Wegovy’s weight-centric titrations.
Monitor for symptoms and report to your doctor; escalation maximizes benefits like sustained appetite suppression.
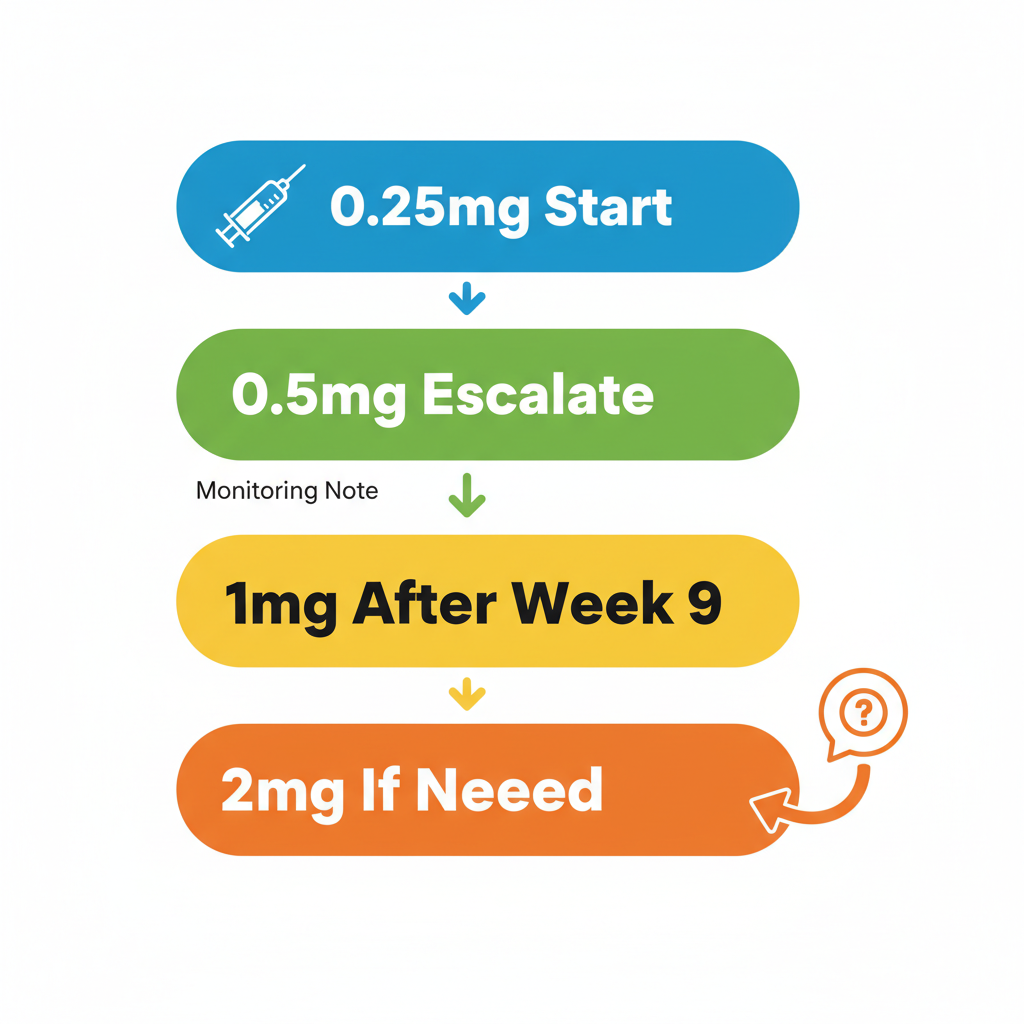
Ozempic dose escalation process from 0.25mg to 2mg weekly
This structured approach not only builds efficacy but also paves the way for enhanced weight loss results when combined with lifestyle changes, as explored in subsequent sections.
Benefits of Ozempic for Weight Loss
Ozempic, a semaglutide-based medication, offers substantial advantages for individuals pursuing weight loss through its GLP-1 receptor agonist mechanism. By mimicking the hormone that regulates appetite and insulin, it promotes sustainable results when used as part of a balanced lifestyle. Adhering to the ozempic dosing frequency guide ensures these benefits emerge gradually, minimizing disruptions and maximizing long-term adherence.
Weight Management Advantages
Ozempic excels in weight management by effectively suppressing appetite and fostering gradual fat loss. Clinical trials, as detailed in reliable medical sources, demonstrate an average weight reduction of 12.4% over 68 weeks with consistent use. This stems from semaglutide benefits for obesity, where the drug slows gastric emptying and signals fullness to the brain, reducing overall calorie intake without extreme dieting.
The weekly dosing schedule plays a pivotal role in maintaining steady hormone levels, which supports sustained appetite control. Patients often report feeling satisfied with smaller portions, leading to effortless portion control over time. For those struggling with obesity, this translates to improved metabolic health and easier integration into daily routines.
To optimize these advantages, pair Ozempic with light exercise and nutrient-dense meals. Consult a healthcare provider to tailor the approach, ensuring safe progression. Following the ozempic dosing schedule by week helps achieve these outcomes predictably.
Side Effects in Context
While pursuing weight loss, users may encounter ozempic side effects weight loss related, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, typically peaking in the first 1-4 weeks as the body adjusts. These gastrointestinal issues arise from the drug’s impact on digestion, but evidence from trials shows they affect about 20-30% of users and diminish with time, allowing focus on positive changes. Overall, these temporary hurdles do not overshadow the transformative potential for most.
GLP-1 side effect mitigation involves simple strategies like starting with lower doses and escalating slowly. Hair loss remains rare and often linked to rapid weight changes rather than the medication itself; severe signs like intense abdominal pain warrant immediate medical attention.
Management tips include eating slowly, staying hydrated, and avoiding fatty foods initially. What are the most common Ozempic side effects for weight loss? Primarily nausea, but how long do Ozempic side effects last? Usually a few weeks with proper care. How to manage nausea from Ozempic? Small, frequent meals prove effective in easing discomfort.
The dosing regimen enhances these benefits by allowing the body to adapt progressively, reducing the intensity of initial reactions. As outlined in clinical data, proper adherence correlates with fewer dropouts and better tolerance. This structured approach underscores why following guidelines leads to smoother experiences.
| Benefit Category | Ozempic Impact | Dosing Role |
|---|---|---|
| Appetite Suppression | Reduces hunger effectively | Weekly Frequency: Supports consistent hormone mimicry |
| Weight Reduction | Up to 15% body weight loss | Escalation Schedule: Gradual increase minimizes dropout |
Data from clinical trials indicate 12-15% weight loss with proper dosing adherence, validating these impacts. The table highlights how Ozempic’s formulation, combined with strategic dosing, outperforms general expectations by promoting steady, manageable progress rather than abrupt changes.
Long-Term Efficacy
Consistent Ozempic use yields enduring benefits, including metabolic improvements like better insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular protection, reducing risks for related conditions. Over 12-18 months, users sustain 10-15% weight loss, with added perks such as lower blood pressure and improved cholesterol levels, as supported by trial outcomes averaging 12.4% reduction.
In comparisons, ozempic vs wegovy dosage reveals similarities since both utilize semaglutide, but Wegovy allows higher maximum doses for potentially greater weight loss in severe cases. Ozempic remains highly effective for dual diabetes and weight management goals. Which is more effective for weight loss: Ozempic or Wegovy? Wegovy edges out for pure obesity treatment, yet Ozempic’s versatility shines for integrated health.
Can Ozempic cause hair loss? It’s uncommon and reversible with nutritional support. To maintain efficacy, track progress quarterly and adjust lifestyle habits. This forward-thinking use ensures lasting vitality beyond initial results.
How Ozempic Works and Dose Escalation
Ozempic, containing the active ingredient semaglutide, plays a key role in managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss through targeted physiological effects. Understanding its mechanism and dosing progression helps patients follow an effective treatment plan.
Mechanism of Action
Ozempic works by acting as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, mimicking the natural incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1. This hormone, produced in the intestines, regulates blood sugar by stimulating insulin release and suppressing glucagon when glucose levels rise after meals. Semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors on pancreatic beta cells, enhancing insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner to prevent hyperglycemia. It also slows gastric emptying, which delays nutrient absorption and promotes a feeling of fullness, aiding appetite control and weight management.
As a weekly injection, Ozempic provides sustained receptor activation, aligning with the ozempic dosing frequency guide that emphasizes consistent levels for optimal efficacy (see ozempic dosing schedule). Clinical insights from sources like WebMD highlight how it ‘mimics incretin hormones’ to improve glycemic control, with studies showing average reductions in A1C by 1-2% over time. This long-acting profile reduces daily fluctuations, making it suitable for patients seeking steady blood sugar and satiety benefits. For those exploring GLP-1 dosing comparisons, Ozempic’s design supports both diabetes therapy and modest weight loss, typically 5-10% of body weight in responsive individuals.
Escalation from Starting Dose
The semaglutide titration strategy begins with a low dose to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Patients start at 0.25 mg once weekly for the first four weeks, allowing the body to adjust. If tolerated, the dose increases to 0.5 mg weekly starting at week five. Further escalation occurs to 1 mg weekly by week nine if additional glycemic control is needed, with some advancing to the maximum 2 mg dose under medical supervision.
This gradual approach, part of the ozempic dosing schedule, helps mitigate common ozempic side effects weight loss related issues like nausea or diarrhea, which often diminish as tolerance builds. Provider oversight is essential during each step, monitoring blood sugar response and side effects through regular check-ins. Trial data from GLP-1 studies indicate that proper escalation improves adherence and outcomes, with over 70% of patients reaching maintenance doses without significant interruptions. Individualized plans consider factors like baseline weight and concurrent medications for safe progression.
Ozempic vs Wegovy Differences
Ozempic and Wegovy both utilize semaglutide but differ in approved uses and dosing parameters, influencing choices for diabetes versus obesity treatment. Ozempic primarily targets type 2 diabetes with secondary weight loss benefits, while Wegovy focuses on chronic weight management in obese or overweight individuals with comorbidities. Both follow weekly subcutaneous injections, starting at 0.25 mg for four weeks to build tolerance, but Wegovy’s escalation includes intermediate steps up to 2.4 mg, higher than Ozempic’s 2 mg maximum, to enhance satiety and fat reduction.
Addressing common queries, Wegovy does not require a higher starting dose than Ozempic; both initiate identically for safety. However, the ozempic vs wegovy dosage variations reflect Wegovy’s emphasis on greater weight loss potential, with trials showing up to 15-20% body weight reduction versus Ozempic’s 10-15%. Direct switching from Ozempic to Wegovy demands consultation due to overlapping but distinct indications and potential adjustment periods. These GLP-1 dosing comparisons underscore the need for personalized prescribing based on health goals.
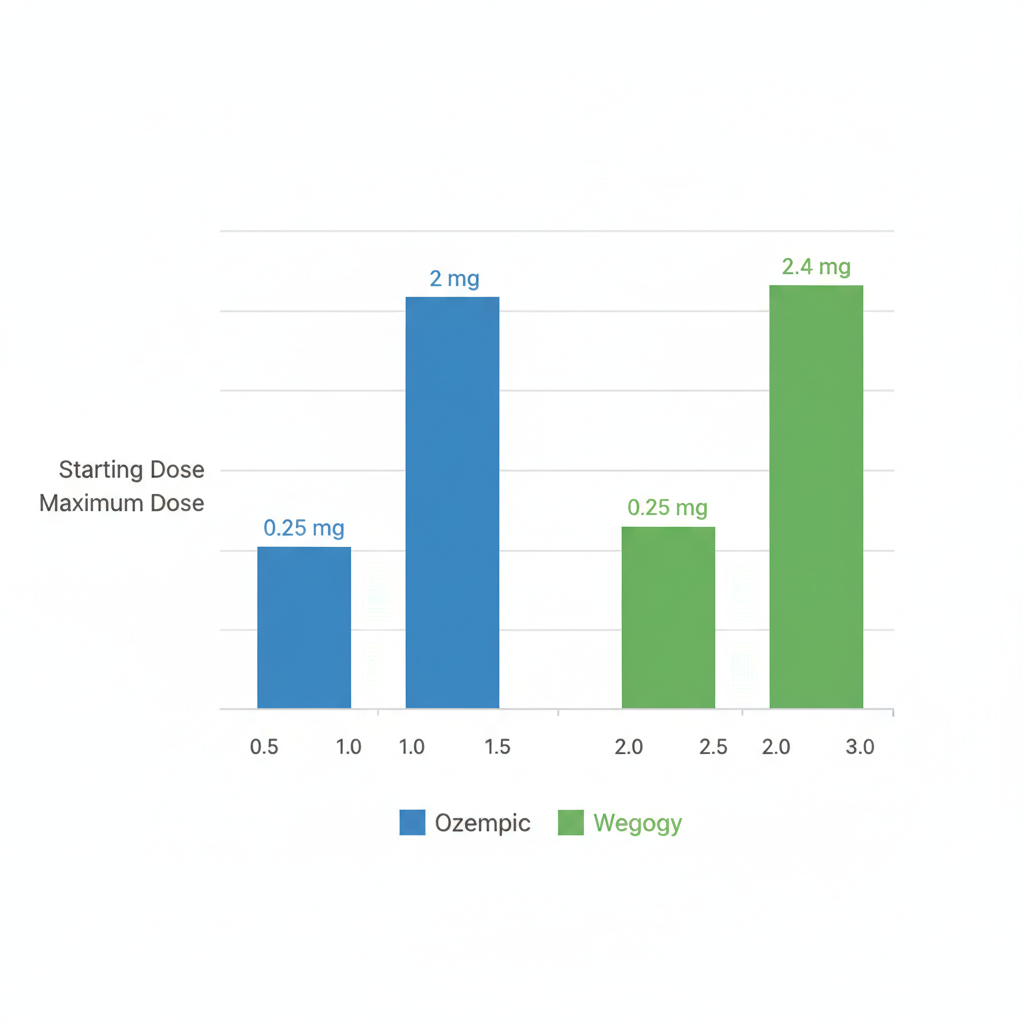
Visual comparison of Ozempic and Wegovy dosage escalations
The image above illustrates these escalation paths, highlighting how Wegovy’s higher ceiling supports intensified weight loss efforts. Comparing dosages helps clarify therapeutic options without assuming interchangeability.
The following table outlines key dosing differences:
| Aspect | Ozempic | Wegovy |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Dose | 0.25 mg weekly | 0.25 mg weekly for 4 weeks |
| Maximum Dose | 2 mg weekly | 2.4 mg weekly after escalation |
Based on FDA labels, Wegovy escalates higher for obesity management. This comparison reveals Ozempic’s suitability for balanced diabetes and weight control, while Wegovy’s profile suits dedicated obesity therapy. Patients should discuss with providers to align dosing with specific needs, ensuring tolerance and efficacy.
Best Practices for Ozempic Dosing and Management
Adhering to your ozempic dosing schedule by week is key to maximizing benefits for weight loss while minimizing risks. These best practices build on semaglutide adherence strategies, offering actionable steps for injectable GLP-1 management. By following these guidelines, you can navigate common challenges and maintain consistent progress.
Handling Missed Doses and Adjustments
If you miss a dose of Ozempic, follow these protocols to stay on track. First, if it’s within 5 days, administer the dose as soon as possible and resume your regular schedule. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take the next one on your scheduled day, avoiding double dosing to prevent complications.
- Check the time since your last injection.
- Administer promptly if under 5 days.
- Skip and resume if over 5 days.
Changing the injection day is possible if needed for your lifestyle. Select a new day with at least 48 hours between doses, aligning with the ozempic dosing frequency guide for safety. For instance, you can shift from Monday to Wednesday without issue. This flexibility supports long-term adherence.
These steps ensure steady semaglutide levels in your body, promoting effective weight loss results. Rationale: Maintaining weekly intervals mimics the drug’s pharmacokinetics, optimizing glycemic control and appetite suppression. Always document changes in a journal for reference.
Warnings: Never take two doses within 48 hours, as this risks overdose symptoms like severe nausea. If unsure, consult your healthcare provider immediately to avoid disrupting your progress.
Managing Side Effects Effectively
Ozempic side effects weight loss often include gastrointestinal issues, but proactive strategies can ease discomfort. Nausea is common initially; start with smaller, bland meals spread throughout the day and stay well-hydrated to reduce intensity. Many users notice improvement within the first few weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Eat slowly and avoid fatty or spicy foods.
- Consider ginger tea or over-the-counter anti-nausea aids after doctor approval.
- Track symptoms daily to identify patterns.
Regarding hair loss myths, Ozempic does not directly cause it. According to WebMD’s Hair Loss Basics, nutritional factors from rapid weight changes are more common culprits, affecting only a small percentage of users indirectly. Focus on a balanced diet to mitigate this.
Emergency signs demand attention: Seek help for persistent vomiting, abdominal pain, or signs of pancreatitis like severe belly pain radiating to the back. For ozempic vs wegovy dosage transitions, similar practices apply, but consult your doctor for personalized adjustments.
These management techniques empower you to handle ozempic side effects weight loss confidently. By addressing issues early, you sustain motivation and adherence, leading to better outcomes over time.
Call your doctor if side effects worsen or persist beyond two weeks.
Monitoring and Long-Term Tips
Regular monitoring is essential for injectable GLP-1 management success. Track your weight and blood sugar levels monthly using a simple app or notebook, noting any trends to discuss with your provider. This helps evaluate if dose escalations are needed based on your response.
- Weigh yourself weekly under consistent conditions.
- Log fasting glucose if diabetic.
- Schedule quarterly check-ins with your doctor.
Integrate Ozempic with lifestyle changes for optimal results: Pair injections with a nutrient-rich diet and moderate exercise, like 30 minutes of walking daily. Semaglutide adherence strategies shine when combined with behavioral support, such as meal prepping or joining a weight loss group.
Long-term, this approach fosters sustainable habits beyond medication. Rationale: Consistent tracking catches plateaus early, allowing timely adjustments for continued efficacy in weight management and health improvement.
Warnings: Do not self-adjust doses; always consult providers for escalations to prevent imbalances. Watch for allergic reactions like rash or swelling, and report them promptly.
By applying these tips, you’re well-prepared for ongoing success with Ozempic.
Key Takeaways for Ozempic Use
The ozempic dosing frequency guide offers a clear semaglutide summary protocol for effective weight management. Start with a low 0.25 mg subcutaneous injection once weekly to minimize side effects, gradually escalating to 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or up to 2 mg as tolerated under medical supervision. Follow the ozempic dosing schedule strictly, administering on the same day each week. If a dose is missed, take it within five days or skip and resume the regular timing–never double up.
Key GLP-1 key insights include substantial weight loss benefits, with users often seeing 5-15% body weight reduction over months when combined with diet and exercise. Common ozempic side effects weight loss experiences involve transient nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal discomfort, which typically fade as the body adjusts. For those considering alternatives, the ozempic vs wegovy dosage comparison reveals similarities in semaglutide action, though Wegovy allows a higher 2.4 mg maximum for more aggressive outcomes.
Manage sides through hydration, small meals, and over-the-counter remedies; always consult your healthcare provider for personalized adjustments, as emphasized in WebMD Ozempic details. Integrate Ozempic into a holistic lifestyle for lasting results–pair with balanced nutrition and activity to amplify benefits.
Disclaimer: This is not medical advice; seek professional guidance before starting. Stay updated with wellness guides–sign up for our newsletter at WellnessHQ.net for tailored tips on weight loss and beyond.

