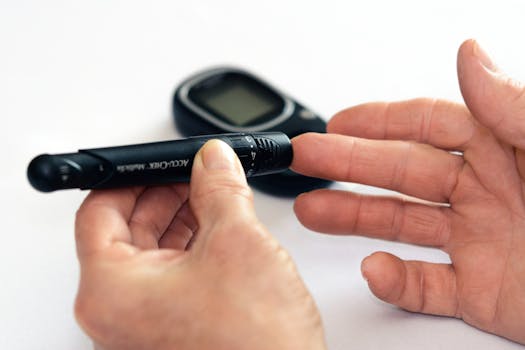
When exploring the topic of caffeine and blood sugar, a common question arises: does caffeine raise blood sugar? This is especially relevant for individuals managing diabetes or those concerned about their blood glucose levels. Understanding how caffeine, particularly from coffee, might impact blood sugar levels is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
How Does Caffeine Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and various medications. Its effects on blood sugar levels are complex and not fully understood. Some studies suggest that caffeine can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels due to its influence on insulin sensitivity. This raises the question: can caffeine raise blood sugar levels significantly?
Research indicates that caffeine may impair insulin action, making it less effective in lowering blood glucose. This effect might be more pronounced in people with type 2 diabetes, where insulin resistance is a key feature. For more insights into diabetes management, you can read our comprehensive guide to managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Does Caffeine Raise Blood Sugar?
The potential of caffeine to raise blood sugar is a concern, especially for habitual coffee drinkers. Evidence suggests that while caffeine does not directly increase blood sugar, it may interfere with the body’s ability to regulate it, particularly after meals. This interaction could possibly affect overall glucose control.
Can Coffee Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
Coffee, one of the most popular sources of caffeine, brings additional compounds into the equation, such as chlorogenic acids, which are known for their antioxidant properties. These compounds might mitigate some of the potential adverse effects of caffeine on blood sugar. However, the presence of sugar, cream, or flavored syrups in coffee can independently raise blood sugar levels.
What Does the Research Say About Caffeine and Blood Sugar?
Studies on caffeine’s impact on blood sugar have yielded mixed results. Some research points to an elevation in blood glucose levels after caffeine consumption, while other studies have found no significant effect. The variation may be due to differences in study design, the form of caffeine consumed, and individual metabolic responses.
An interesting factor is the body’s adaptation to regular caffeine intake. Long-term coffee drinkers may develop a tolerance, potentially reducing the blood glucose response seen in occasional caffeine consumers. For more scientific insights, you can refer to this comprehensive article on Wikipedia.
Considerations for Individuals with Diabetes
For those with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is critical. The effects of caffeine may require personal observation and adjustment. Monitoring blood glucose levels after consuming caffeinated beverages can help individuals understand their personal response to caffeine and manage their diet accordingly.
How to Enjoy Coffee Without Spiking Blood Sugar
If you’re a coffee enthusiast concerned about blood sugar control, consider consuming coffee in moderation. Opt for black coffee or use non-caloric sweeteners and almond or oat milk instead of sugar and cream. These alternatives may help minimize the potential impact on your glucose levels.
While direct evidence that caffeine elevates blood sugar to concerning levels remains mixed, it is wise to remain cautious. Observing how your body reacts after caffeine consumption ensures control over dietary impacts on blood sugar.
- Caffeine may affect blood sugar levels through its impact on insulin sensitivity.
- The effects of coffee on blood sugar are influenced by individual tolerance.
- Moderation is key to consuming caffeine without significant glucose spikes.
- Personal blood glucose monitoring can aid diabetic individuals in managing caffeine intake.
FAQs
Is it safe to drink coffee if I have diabetes?
Yes, many individuals with diabetes drink coffee. However, it’s crucial to monitor how your blood sugar responds. Discuss your dietary choices with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How much caffeine is safe for daily consumption?
Most dietary guidelines suggest up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day for adults, equivalent to about four 8-ounce cups of brewed coffee, may be safe for most people.
Can decaffeinated coffee affect blood sugar levels?
Decaffeinated coffee contains minimal caffeine and may have a lesser effect on blood sugar compared to regular coffee, but other factors (like sugar) can still influence blood sugar levels.
Do all caffeinated beverages affect blood sugar similarly?
No, different beverages contain varying amounts of caffeine and other substances that can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism differently.
Does caffeine increase the risk of diabetes?
There is no conclusive evidence that caffeine increases the risk of developing diabetes. Some studies even suggest a protective effect of coffee consumption.
In summary, while the question “does caffeine raise blood sugar” remains complex, understanding individual reactions and maintaining healthy dietary habits can help manage any potential impact on blood glucose levels effectively.