Understanding the concept of body reconstruction can provide valuable insights into the realm of medical procedures aimed at restoring the body’s function and appearance. This process encompasses a variety of surgical techniques designed to correct physical abnormalities caused by trauma, congenital defects, tumors, or surgeries such as mastectomies. By exploring the diverse options within this field, individuals can feel more informed and prepared when considering their reconstructive needs.
What Is Body Reconstruction?
Body reconstruction, often referred to as recon surgery or reconstruction plastic surgery, is a specialized branch of surgery that focuses on repairing and reshaping body structures. These surgeries can be necessary following injury, disease, or congenital issues, seeking to restore not only appearance but also function. Techniques in reconstructive surgery are advanced and can vary significantly based on the area of the body and the specific needs of the patient.
Types of Reconstructive Surgeries
There are numerous types of reconstructive surgeries, each tailored to specific conditions and needs. Some common examples include breast reconstruction following mastectomy, cleft lip and palate repair, and reconstructive hand surgery. These procedures are not limited to aesthetics; they often play a critical role in improving a patient’s quality of life by restoring functionality.
Breast Reconstruction
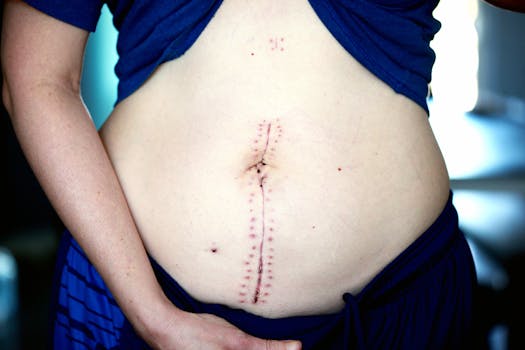
Breast reconstruction surgery is commonly associated with restoring breast shape following mastectomy due to cancer. Surgeons may use implants or tissue from other parts of the patient’s body, a method known as autologous or flap reconstruction, to create a natural appearance. More information about related procedures can be found in our article on what to expect from fat transfer breast augmentation.
Hand and Face Reconstruction
Reconstructive surgery also extends to the hands and face, where it can address injuries from accidents or correct birth defects. Surgical interventions can repair tendon damage or mitigate facial trauma effects, enhancing both the aesthetic and functional aspects of these areas. Successful outcomes often require a personalized approach, employing both surgical expertise and artistic precision.
Skin and Tissue Reconstruction
A major aspect of reconstructive surgery involves the repair of skin and tissue, often necessary after significant weight loss, trauma, or burns. Skin grafts and flaps are techniques used to cover defects and encourage healing, exemplifying how surgical reconstruction can facilitate recovery and improve patients’ physical comfort and mobility.
The Process of Reconstructive Surgery
The journey of reconstruction plastic surgery typically begins with a detailed consultation. During this phase, a surgeon will evaluate the patient’s condition, discuss potential outcomes, and tailor a surgical plan that aligns with the patient’s goals and health status. Preoperative preparations, anesthesia considerations, and possible risks are key factors deliberated in the planning stage.
Surgical Techniques and Innovations
Reconstructive surgery employs various techniques, from traditional methods like skin grafts to innovative approaches involving 3D printing and tissue engineering. Surgeons continually integrate new technologies to enhance precision and improve patient outcomes. Advances in microsurgery, for example, have revolutionized procedures, enabling intricate repairs of nerves and small vessels.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from surgical reconstruction is as crucial as the surgery itself. It requires adherence to a comprehensive care plan encompassing physiotherapy, follow-up consultations, and monitoring for complications such as infections or wound healing issues. Patience and perseverance during this phase are vital, as healing can be gradual.
Understanding what is reconstructive surgery highlights its profound impact not only in restoring appearance but significantly enriching a patient’s functional capacity. Encouragingly, the field continues to evolve, promising even more refined results for patients seeking restorative procedures.
- Body reconstruction is crucial for repairing and reshaping various body structures.
- Breast, hand, and facial reconstructions are among the most common types.
- Innovations like 3D printing continue to advance the field.
- Consultation and personalized approaches are key to success.
- Recovery requires commitment to aftercare and follow-up.
What is the primary goal of body reconstruction?
The primary goal of body reconstruction is to restore functionality and appearance to body parts affected by congenital, traumatic, or surgical changes, thus enhancing patients’ quality of life.
Can reconstructive surgery be performed alongside cosmetic surgery?
Yes, reconstructive surgery can be performed alongside cosmetic procedures, often in cases where function and aesthetics are both considered, ensuring that patients achieve their desired physical results.
Who is a good candidate for reconstructive surgery?
A good candidate for reconstructive surgery is someone in overall good health, with realistic expectations and a comprehensive understanding of the risks and benefits, as assessed by a qualified surgeon.
How long is the recovery period following reconstructive surgery?
The recovery period can vary widely depending on the type of surgery, from a few weeks to several months. It is important to follow the surgeon’s guidance on post-operative care to ensure optimal healing.
Are there non-surgical alternatives to body reconstruction?
In some cases, non-surgical treatments like physical therapy or orthotics may complement or, in less severe cases, be alternative options to surgery, depending on the individual’s condition and goals.