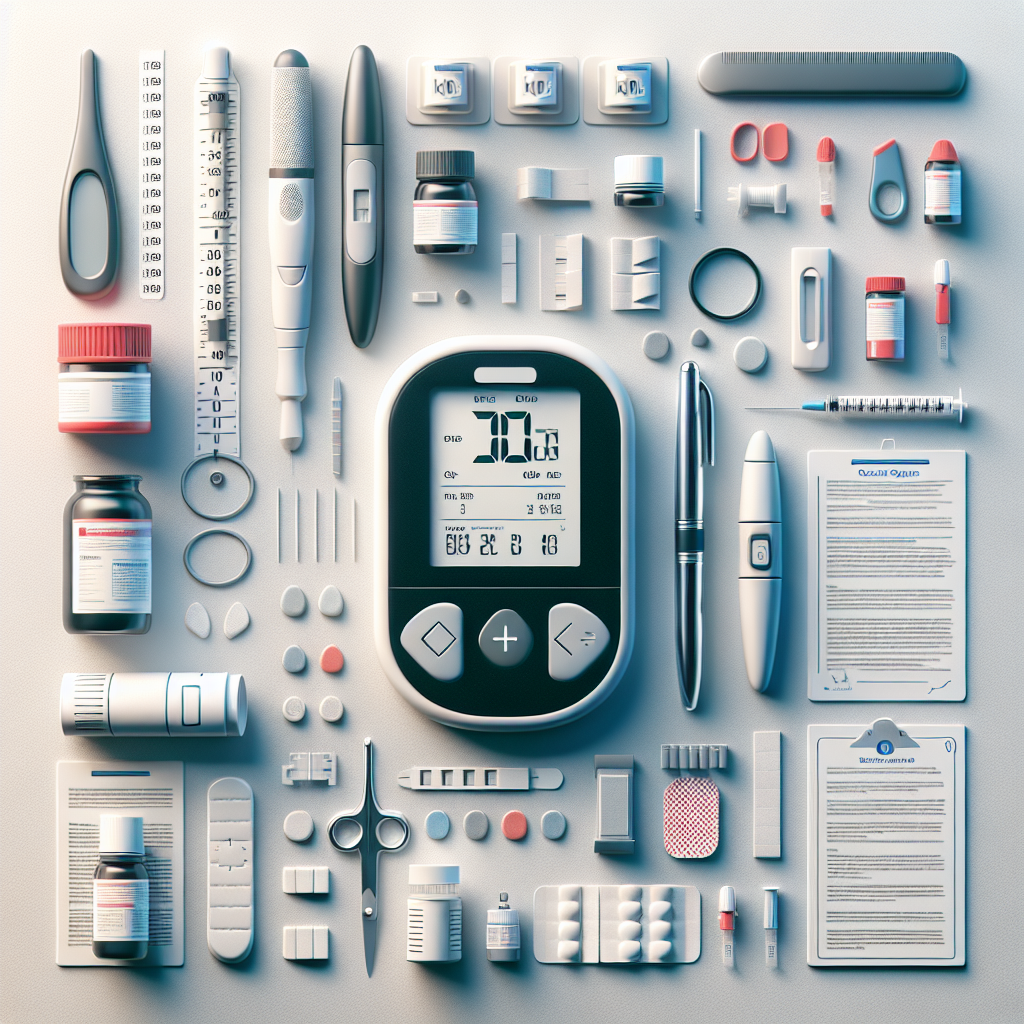
Choosing the right device for home monitoring can feel overwhelming. A blood glucose level testing kit is often the first tool people reach for when they need to track sugar levels at home, but there are many options—lancet-based meters, meters with Bluetooth, and even continuous sensors. This guide explains the differences between common devices, how to read results, and what to consider when buying or using a kit.
Blood glucose testing kits: types and how they work
Most personal devices use a small pinprick to collect a drop of blood and a blood glucose meter or blood sugar meter to display a numeric result. Traditional blood glucose machines and blood sugar machines are sometimes called blood test machines or blood meter kits. Newer alternatives include continuous glucose monitoring and glucose sensor patch systems that read interstitial fluid continually rather than relying on fingersticks.
Fingerstick meters vs continuous systems
Fingerstick tools include the blood glucose monitor, the blood meter, and variations like glucose meter kit and blood meter kit. These blood glucose meters or blood sugar test kits are reliable for spot checks. By contrast, a glucose monitor kit or glucose sensor patch is designed for ongoing monitoring and can show trends over time. People often ask about how to get a cgm without diabetes; availability depends on local regulations and insurance, and many suppliers require a prescription.
Choosing the right device
When comparing options, think about accuracy, ease of use, and cost. Consider a blood glucose monitoring kit if you want an all-in-one package that includes test strips and a lancing device. A blood sugar check kit might be adequate for occasional checks, while a continuous glucose monitor or a glucose test meter is better for frequent tracking. If cost is a concern, compare the price of diabetic meters and test strips across brands and the ongoing expense of diabetic test meters.
Key features to compare
- Accuracy and FDA approval — verify test strips and meters are cleared.
- Cost of test strips for blood glucose meters and diabetic meters and test strips.
- Connectivity and apps (some blood glucose monitors can sync to smartphones).
- Comfort — lancing devices, blood sugar testing meter design, and alternate-site testing options.
- Availability of glucose meter kit accessories like spare lancets and control solution.
How to use your device safely and effectively
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your blood sugar monitor or blood sugar test kit. For a fingerstick: wash and dry your hands, use a fresh test strip in the blood sugar meter, apply the blood drop to the strip, and record the reading. If you use a continuous sensor, learn how to apply the glucose sensor patch correctly and how to calibrate if required. For both methods, keep a log of readings and note glucose trends or unusual values.
Interpreting results and tracking trends
Spot checks with a glucose meter, blood glucose monitor, or blood sugar meter give single values; continuous devices show trends and levels cgm over time. If you see consistent highs or lows on a blood sugar testing meter or glucose monitor kit, consult your healthcare team to adjust medication, diet, or activity. Remember that hydration, illness, and certain medications can affect readings on your blood sugar machine or blood test machine.
Where to buy and what to ask
You can buy blood glucose machines, blood glucose meters, and glucose test kits at pharmacies, medical supply stores, and many online retailers. When selecting a blood sugar machine or glucose meter kit, ask about warranty, the cost and availability of test strips, and whether the device supports data export. If you’re exploring a continuous glucose monitoring option, talk about sensor supplies and how often the glucose sensor patch must be replaced.
For broader context on diabetes management and monitoring recommendations, reliable public health resources can help; see the CDC’s overview of diabetes basics for trusted guidance: CDC — Diabetes Basics and Monitoring.
If you want a deeper look at treatment approaches for both major types of diabetes, including how monitoring fits into overall care, review this comprehensive guide on treatment options and care strategies: comprehensive guide to type 1 and type 2 diabetes treatments for 2024.
Quick checklist before purchase
- Confirm compatibility of test strips with your blood glucose meter or blood sugar test kit.
- Estimate monthly cost for diabetic meters and test strips or for replacement glucose sensor patches.
- Consider whether you need advanced features like Bluetooth or a full blood glucose monitoring kit.
FAQ
Q: How accurate are home glucose meters compared to lab tests?
A: Modern blood glucose meters and blood sugar testing meters are generally accurate for routine monitoring, but lab tests remain the standard for diagnostic precision. If you get unexpected or inconsistent results, repeat the test and consult a provider.
Q: Can continuous glucose monitoring replace fingersticks?
A: Many people reduce fingersticks after starting continuous glucose monitoring, but some CGM systems still recommend occasional fingerstick checks with a blood sugar meter or glucose test meter for calibration or confirmation.
Q: What should I do if my readings are very high or low?
A: If you have extreme values on your blood sugar monitor or blood sugar test kit, follow your healthcare plan’s emergency instructions and contact medical help if symptoms are severe or persistent.