Understanding the management of diabetes mellitus is crucial for the health and well-being of those diagnosed with this condition. Managing diabetes effectively can help prevent complications and lead to a healthier lifestyle. This guide provides an overview of how diabetes can be managed through various approaches including medication, diet, exercise, and monitoring.
Understanding the Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, requires careful and consistent management to prevent health complications. The management of diabetes mellitus involves maintaining a balance between medication, diet, and lifestyle to achieve optimal blood glucose control.
1. Medication and Insulin Therapy
For many diabetes patients, medication is an essential element of managing their condition. Type 1 diabetes typically requires insulin therapy, which involves the administration of insulin injections or an insulin pump. For type 2 diabetes patients, oral medications or insulin may be prescribed depending on the severity of the diabetes and the individual’s response to other treatments. As always, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan tailored to your needs.
2. Nutrition and Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in diabetes management. A balanced diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight. It is recommended to focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Monitoring portion sizes and carbohydrate intake is particularly important. Engaging with a dietitian can provide personalized dietary recommendations and meal planning tips.
3. Regular Exercise
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can significantly impact how to manage type 2 diabetes. Exercise aids in lowering blood glucose levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and contributing to weight maintenance or reduction. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can be a beneficial target for diabetes patients.
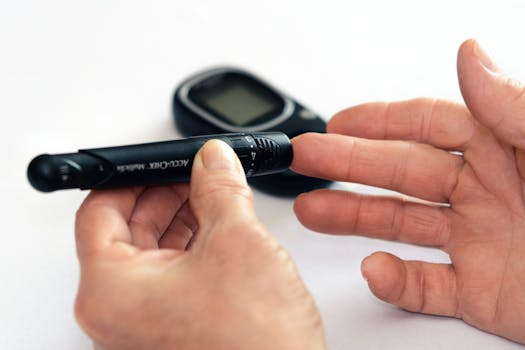
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is fundamental for living with diabetes. Self-monitoring helps track how lifestyle factors and treatment plans affect glucose levels, enabling timely adjustments. Some individuals may require continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices that provide real-time insights and alerts. Consult with a healthcare professional to understand the best monitoring strategy for you.
5. Lifestyle Considerations
Beyond medication and diet, other lifestyle choices impact diabetes management. Stress management is crucial as stress can affect blood glucose levels. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and breathing exercises may help reduce stress. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake also contribute to better diabetes control.
6. Importance of Education and Support
Education plays a central role in diabetes management. Understanding your condition and its potential complications empowers you to make informed decisions. Support groups and counseling can also provide valuable resources and emotional support to those managing diabetes.
For further reading, you may visit a comprehensive resource on health and how it relates to diabetes management and overall well-being.
Conclusion
The comprehensive management of diabetes mellitus encompasses a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments. By maintaining informed and vigilant care practices, diabetes patients can lead healthier lives while minimizing the risk of complications.
- Effective diabetes management involves medication, diet, exercise, and monitoring.
- Personalized treatment plans should be developed with healthcare providers.
- Diet and exercise are critical components in managing glucose levels.
- Regular blood sugar monitoring helps in maintaining control over diabetes.
- Education and support are essential in everyday management.
FAQ
What are the most common medications for diabetes management?
Common medications include Metformin for type 2 diabetes and insulin therapy for type 1 diabetes. Other medications may include newer injectables and oral drugs. Always consult a healthcare provider for individual recommendations.
How can diet affect diabetes management?
Diet plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels. A diet rich in fiber, lean protein, and low in processed carbohydrates can support better glucose control and overall health.
What types of exercises are recommended for people with diabetes?
Moderate aerobic exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are recommended. These activities can help improve insulin sensitivity and support weight management.
How frequently should blood glucose levels be monitored?
The frequency of monitoring depends on the type of diabetes and individual health plans. Generally, monitoring may be done several times a week or daily, especially when managing insulin-dependent diabetes.
Can stress management contribute to better diabetes control?
Yes, stress can affect blood glucose levels. Employing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga may contribute positively to diabetes management.