Understanding blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining optimal health, especially for individuals managing diabetes. A normal blood sugar levels chart can be a valuable tool for tracking glucose levels and ensuring they remain within a healthy range. This article provides insight into how to use these charts, their significance, and how they relate to various factors like age, meal times, and A1C results.
Understanding the Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
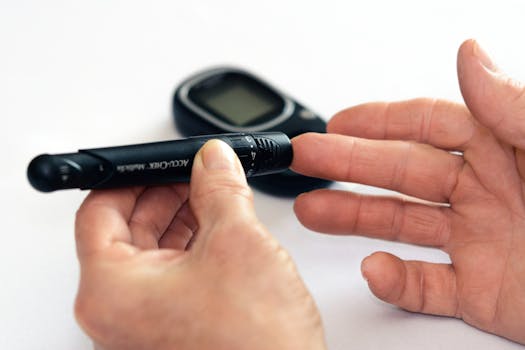
A normal blood sugar levels chart helps individuals and healthcare providers monitor and manage blood sugar effectively. These charts categorize glucose readings into pre-meal, post-meal, and fasting levels, all of which are crucial for comprehensive blood sugar management. By understanding these ranges, you can better assess your overall health and adjust your lifestyle or treatment plan accordingly.
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting blood sugar, tested after an overnight fast, is a key indicator of how well your body manages glucose. Ideal fasting levels usually range from 70 to 99 mg/dL. However, this can vary depending on factors such as age and health conditions. For example, adults aged 50 to 60 may experience slight variations, as indicated in a blood sugar level age 50 to 60 chart.
Blood Sugar After Meals
After consuming food, blood sugar levels rise temporarily. A blood sugar after meal chart assists in tracking these levels, with normal readings often falling below 140 mg/dL two hours post-meal. Monitoring postprandial glucose can provide insights into how your body processes carbohydrates.
A1C and Glucose Correlation
The A1C test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. An A1C to blood sugar table is helpful in converting these percentages into average glucose levels, offering a broader view of blood sugar control. For example, an A1C of around 6.5% is approximately equivalent to an average blood glucose level of 140 mg/dL.
The Role of Age in Blood Sugar Levels
A blood glucose level chart by age helps in understanding how normal ranges might shift as individuals grow older. While younger adults typically maintain stricter glucose control ranges, older adults may require adjustments to account for other health conditions or medications. A normal blood sugar levels chart by age can guide these adjustments.
How to Use Blood Sugar Charts Effectively
Utilizing a blood glucose levels chart effectively requires regular monitoring and documentation. You can use a blood glucose level chart printable version to track daily readings, alongside any dietary changes or medication adjustments. This ongoing log helps identify trends and patterns that require attention.
Additionally, individuals with diabetes may benefit from resources provided in our comprehensive diabetes management guide, which includes further strategies for maintaining healthy glucose levels.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar
Regularly checking blood sugar levels is critical for preventing complications associated with diabetes and maintaining general well-being. Charts such as the insulin level chart or the non fasting blood sugar levels chart offer a comprehensive approach to monitoring, even when not in a fasted state.
Resources for Blood Sugar Management
Several online and healthcare resources provide detailed charts and conversion tables, such as the A1C conversion table or the hemoglobin A1C and blood glucose chart. These tools aid in translating clinical results into actionable insights for better health outcomes.
Moreover, understanding the eAG (estimated Average Glucose) normal range can bridge the gap between A1C results and daily glucose readings, offering another perspective on blood sugar management.
These comprehensive charts not only assist those currently managing diabetes but also serve as educational tools for individuals looking to understand their glucose metrics and take proactive steps toward health optimization.
- A normal blood sugar levels chart helps track glucose for better health management.
- Fasting, post-meal, and A1C levels are crucial components of these charts.
- Age, meal timings, and A1C results can influence normal blood sugar ranges.
- Effective monitoring can prevent complications and guide treatment adjustments.
- Charts are valuable educational resources for managing and understanding blood sugar.
What are normal blood sugar levels?
Normal fasting blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 99 mg/dL for adults, while post-meal levels should be below 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How is the A1C test used to measure blood sugar control?
The A1C test measures average blood glucose levels over a two to three-month period, expressed as a percentage that can be translated into estimated average glucose levels using a blood glucose to A1C chart.
Can blood sugar levels vary by age?
Yes, blood sugar levels can vary based on age and overall health. A blood sugar levels chart by age helps understand normal ranges and necessary adjustments for different age groups.
How can I use a blood sugar chart effectively?
By regularly monitoring and documenting blood sugar readings, identifying trends, and adjusting lifestyle or treatment plans as needed, one can effectively use a normal blood sugar levels chart to manage health.
Where can I find reliable blood sugar conversion tools?
Resources such as the CDC or National Institutes of Health provide reliable conversion tables and educational information on managing blood sugar levels effectively.
For further information, engaging with detailed resources on blood sugar management, like the normal blood sugar levels chart, can empower individuals to take control of their health. Such tools and insights foster better understanding and management of glucose levels for a healthier life.